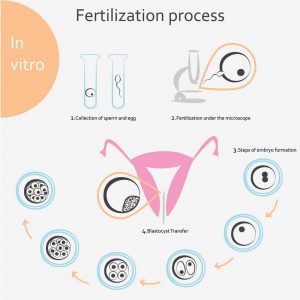
In Vitro Fertilization
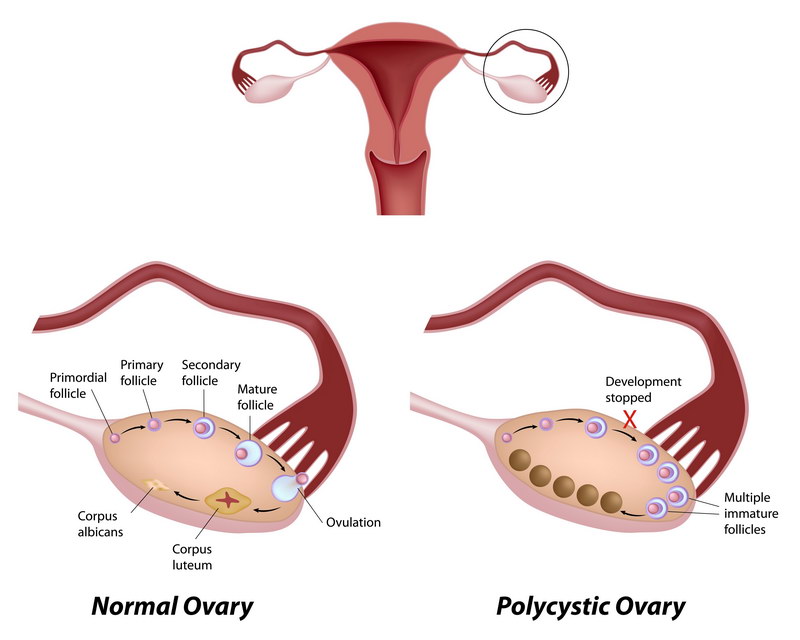
Polycystic Ovarian Disease
Polycystic Ovarian Disease
The Polycystic Ovarian Disease or PCOS is a condition where the levels of progesterone and estrogen in a woman are imbalanced, leading to the growth of benign mass on the ovaries or ovarian cysts. Having the Polycystic Ovarian Disease can cause you a variety of problems when it comes to your menstrual cycle, cardiac function, fertility, and appearance. Based on reports from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, about one in ten and one in twenty childbearing women of age suffer from the Polycystic Ovarian Disease; and currently, about five million women are affected by this in the United States.
Causes of Polycystic Ovarian Disease
The exact cause of Polycystic Ovarian Disease is still unknown but doctors believe that genetics and hormonal imbalances play a vital role when it comes to the disease; the most common individuals to develop PCOS are women whose mother or sisters have the disease.
Another contributing factor to the Polycystic Ovarian Disease is the overproduction of androgens a male sex hormone that can be produced by women. If you ever have Polycystic Ovarian Disease, you will notice that you usually produce much higher levels of this male sex hormone that greatly affects the growth and release of eggs during the ovulation period. Too much insulin a hormone that transforms starch and sugar into energy can cause increased levels of androgen.
Symptoms of Polycystic Ovarian Disease
The symptoms of Polycystic Ovarian Disease begin gradually and the hormonal changes leading to PCOS usually occur at the early teens stage, right after their first menstrual period; you should also remember that the symptoms of PCOS are highly noticeable right after gaining weight. Here are the other symptoms of the Polycystic Ovarian Disease:
1. Menstrual issues which can include just a little or no periods at all, or irregular and heavy bleeding.
2. Hair loss on the scalp and hirsutism which is the growth of hair on the face, back, chest, thumbs, stomach, or even the toes.
3. Oily and acne-filled skin.
4. Fertility issues like not ovulating or repeated miscarriages.
5. Mood swings or depression.
6. Hyperinsulinemia (excessive levels of insulin) and insulin resistance these can cause reactions such as skin tags and upper body obesity.
7. Breathing issues while sleeping or more commonly known as obstructive sleep apnea; this is generally connected to both insulin resistance and obesity.
What Happens During Polycystic Ovarian Disease
Polycystic Ovarian Disease usually affects your reproduction and how your body regulates sugar; it also affects how your heart functions. Aside from these, here are the other things that happen when you have Polycystic Ovarian Disease:
Reproductive Issues
Hormonal imbalances bring about different types of pregnancy issues and problems which include:
1. Infertility which happens when your ovaries do not release eggs every month.
2. Repeated miscarriages.
3. Increased levels of blood pressure during delivery or pregnancy; having a smaller or larger than normal baby, or even having a premature child.
4. Pre-cancer of the lining of your uterus which is called endometrial hyperplasia; this usually occurs when you have irregular menstrual cycles since regular cycles usually clear off and build up the uterine lining every month.
5. Endometrial cancer is possible when you have Polycystic Ovarian Disease and the usual risk is during the reproductive years. During this period, it is about three times riskier for women with PCOS compared to those who ovulate regularly.
Blood Sugar Issues
Insulin is known as a hormone that aids the cells in your body to acquire adequate amounts of sugar necessary to get energy. There are times when these cells do not completely react to insulin and this is called insulin resistance; insulin resistance can lead to diabetes.
Stroke and Heart Problems
Increased insulin levels from Polycystic Ovarian Disease can automatically lead to blood vessel and heart problems which include atherosclerosis (hardening of ones arteries), high blood pressure, heart attack, coronary artery disease, high cholesterol, and stroke.
Complications of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
If you have PCOS, you have higher chances of developing the following:
1. High blood pressure or hypertension
2. Anxiety and depression
3. High-cholesterol
4. Heart attack
5. Diabetes
6. Sleep apnea a condition when a person periodically stops breathing while asleep
7. Breast cancer
8. Endometrial cancer cancer that is caused by the thickening of your uterus lining.
Treatment and Prevention
Having a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, following weight control, and not smoking are some of the most vital parts of treating Polycystic Ovarian Disease; you can also take certain medications to evenly balance out your hormones. The type of treatment generally depends on your symptoms and whether you plan to get pregnant.
Unfortunately, there really is no cure for PCOS but controlling this can lower your chances of miscarriages, infertility, heart disease, diabetes, and even uterine cancer.
Empower Fertility

Support for Couples Through Fertility Treatment

How to Choose the Best Fertility Doctor

How to Deal with Stress during Treatment

How to Boost Your Self-esteem During Treatment

How to Experience Happiness and Calm During Pregnancy

How to Nurture your Relationship During Fertility Treatment

Methods of Coping During Fertility Treatment